Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor: What It Is, How It Works, and What It's Used For
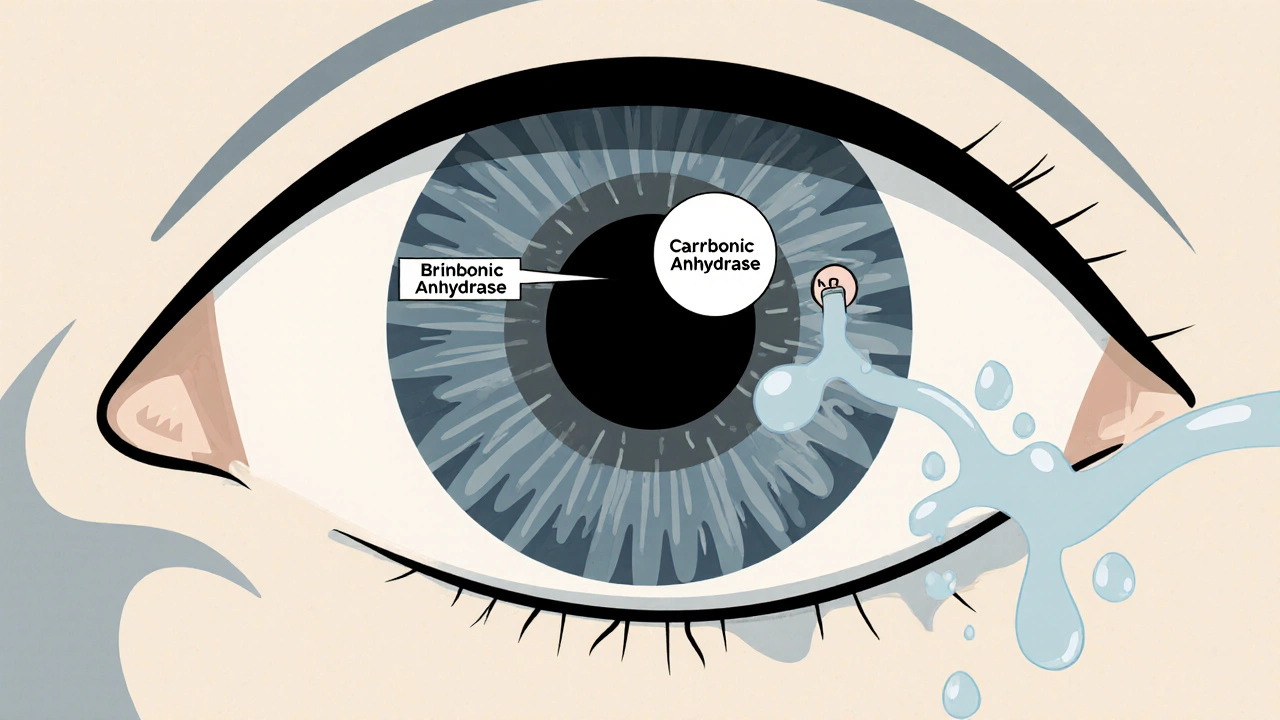
When you hear carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, a type of medication that blocks an enzyme involved in fluid and acid balance in the body. Also known as CAI, it doesn’t sound like something you’d take unless you have a specific condition — and that’s mostly true. These drugs aren’t for everyday use, but they’re crucial for people dealing with glaucoma, altitude sickness, or certain types of seizures. They work by slowing down the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, which helps your body manage how much fluid and acid builds up in places like your eyes, kidneys, and brain.
Think of carbonic anhydrase like a faucet that lets fluid flow where it shouldn’t. In glaucoma, too much fluid builds up in the eye, raising pressure and damaging the optic nerve. A carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, a medication that reduces fluid production in the eye turns that faucet down. In altitude sickness, your body struggles to adjust to thin air, causing headaches and nausea. Here, the same drug helps your kidneys flush out bicarbonate, making your blood slightly more acidic — which tricks your body into breathing deeper and getting more oxygen. For epilepsy, it stabilizes electrical activity in the brain by changing how ions move across nerve cells.
These drugs aren’t one-size-fits-all. acetazolamide, the most common carbonic anhydrase inhibitor, used for glaucoma and altitude sickness is often the first choice. But others like methazolamide or dorzolamide (eye drops) are used when you need local effects without systemic side effects. Side effects? You might get tingling in your fingers, a metallic taste, or more frequent urination — because it’s a diuretic. Some people feel tired or lose their appetite. These aren’t dangerous for most, but they’re not harmless either. People with kidney disease, sulfa allergies, or severe liver problems need to avoid them.
What you’ll find in the posts below isn’t a textbook on biochemistry. It’s real-world insight from people who’ve taken these drugs, doctors who’ve prescribed them, and studies that show what actually works. You’ll see how carbonic anhydrase inhibitor fits into daily life — whether it’s managing eye pressure after surgery, preparing for a mountain climb, or dealing with side effects that no one warned you about. There’s no fluff here — just what matters when you’re trying to stay healthy while using a drug that doesn’t get much attention but changes lives when it works.